Review Article: 2024 Vol: 28 Issue: 3S
A Pragmatic Analytical Approach Determining the Role of Green Fmcg Consumers??? Perception in Increasing Adaptability of Green Fmcg Products
Anjali D Manglani, Mudra Institute of Communications Ahmedabad, Gujarat
Rahulkumar M. Dhruv, Smt. C.C Mahila Arts and Sheth C.N. Commerce College, Visnagar
Hayri Uygun, Recep Tayyip Erdogan University Rize Turkey
Rashmi Gujrati, Principal (KCSMCA) Campus Director KC Group of Institutions
Rajesh M Patel, Dean Sachkhand Patel University Vishnagar
Citation Information: Manglani, A.D., Dhruv, R.M., Uygun, H., Gujrati, R., & Patel, R.M. (2024). “A pragmatic analytical approach determining the role of green fmcg consumers’ perception in increasing adaptability of green fmcg products”. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 28(S3), 1-9.
Abstract
Purpose: Climate crisis is one of the contemporary issues in today’s era and green marketing is one of the feasible solutions for industrial pollution contributing to climate crisis. The industry is moving towards sustainable development and green marketing is one of the salient solutions that helps in attaining it. Green marketing is a broad concept including the entire life cycle of a product starting from the green manufacturing to green packaging. It is necessary to generate green awareness to chase the adaptability of green products which can ultimately contribute to environment conservation. Consumers are adopting green products for the daily usage as awareness is increasing day by day. Along with consumer’s awareness, it is necessary to identify consumers’ perception which revolves around the consumer’s purchase decision. This research has tried to analyse the association between demographic variables and green FMCG aware consumers’ perception regarding green marketing practices in Gujarat. Design/ Methodology/ Approach: The study adopted a structured questionnaire for collecting data among 368 green FMCG consumers of Gujarat through convenience sampling technique and analysed data with Cross tabulation analysis, Chi-square test and Frequency distribution analysis. Prior to the final data collection, a pilot testing was conducted among 200 FMCG consumers of Gujarat for comprehensive analysis of identified parameters for consumers’ perception from secondary research. Findings: The findings of study described that all the demographic variables have significant association with selected consumers’ perception. The study determined a niche target market from Gujarat’s green FMCG consumer market and established the conceptual relationship among green consumers’ perception influencing the green purchase decision. Originality: A unique linkage established between consumers’ perception describing their dependency on each other for making purchase decision. The study has tried to contribute uniquely by describing the group of target audience which marketers can focus upon to expand the reach in market of green FMCG products.
Keywords
Green Marketing, Sustainable Development, Sustainable Lifestyle, Green Awareness, Green Consumers’ Perception.
Introduction
Green marketing is, significantly, a process of developing a product pertaining eco-friendly attributes with least negative impact on environment and it is necessary to advertise those products based on their perceived environmental values Ali, et al. (2018); Ayyappan et al. (2023). Now days, consumers’ awareness and consciousness towards environment conservation strongly push companies towards their green commitment. For instance, the eco-resorts/hotels globally, are initiating to recognize themselves with attribute "ecotourism" describing their green initiative to encounter nature by limiting their negative ecological footprint. In this manner green showcasing consolidates a wide scope of exercises, including product alteration, changes to the creation cycle, bundling changes, as well as altering promoting Fouziya & Gracious (2018). Studies reflect that 77% of consumers believes and prefers to choose brand which are sustainably and environmentally responsible. Indian consumers nearby 60% are willing to pay premium prices for eco-friendly products and 52% of urban Indian consumers are likely to hike their expenses on green brands over the next three years (Upgrade, 2023).
Several marketing strategies are identified which can help building a green brand, i.e., Sustainable Design with cradle-to-cradle life cycle process of a product practicing least waste and ethical procurement, Socially Responsible behaviour towards green brand and society, Green Pricing Justification, and Practicing green practices initiatives ethically and gaining consumer loyalty. These strategies immensely influence the consumer behaviour (Emeritus, 2023). Hesil Jerda, (2020) Green marketing can be absolute effective, if practiced rightly. According to the Bain report, Awareness and environmental consciousness made sustainability a matter of concern among Indian consumers. The researchers found that only 20% of Indian consumers are socially and environmentally conscious, whereas 49% are health conscious. There is the need of generating environmental consciousness among consumers and make them understand the correlation between environmental health and human health. This consciousness among consumers can expand green products’ reach in society and help establishing green market ethically with foreseen environmental conservation practices and determined results, as study claims environmental concern has triggered aware Indian consumers to wisely choose sustainable products above all other products (Emeritus, 2023); ITC. (2020); ITC. (2021).
Green consumers’ perception holds a vital role in determining their purchase behaviour. Also, to comprehend consumers’ perception in a crystalline manner it is necessary to associate them with attributes of target market. The study has made an attempt to study the group of FMCG consumers of Gujarat as it is the state of tradition pertaining several eco-friendly attributes among their culture Janda et al. (2022); Ker et al. (2019); (Patel, 2018). The present study tried to examine the association of green consumers’ perception with the demographic variables of green FMCG consumers of Gujarat.
Literature Review
It determined that consumers were not aware about green initiatives undertaken by various governmental and non-governmental agencies. Consumers were found having concern towards depletion of ozone and global warming. The study recommended adopting such advertisements which appeals using green products and practices, which were likely to touch emotions of consumers. Constant communication from the company is required to make an impact and create a distinct green positioning suggested that company could adopt green practices by providing training to their employees which made them knowledgeable as well as foreground promotion of green products effectively.
Rajamanickam (2022) suggested that company should ensure that green products were of high quality with competitive price, also should design the marketing communication campaigns to promote green products. Fouziya & Gracious J (2018) revealed the significance and necessity of crystalline the consumer’s perception. Study recommended companies to use environment friendly raw materials and recyclable energy for production, develop a green business culture, recyclable packaging materials, and eco-friendly labels identified the main sources generating awareness among consumers about green products. The findings revealed that print media and websites of the companies were the main sources and eco-friendly vehicles, and organic food were the main products purchased by ecofriendly consumers. revealed that people strongly agree with the information availed for a green product but expected product’s performance was identified as the main barrier in the making purchase decision for a green product revealed that the key to increase green product purchase intention among the generic public, depended upon four factors which were environment, social influence, health consciousness, and perceived consumer effectiveness. Rajamanickam (2022) has suggested that company should ensure that green products were of high quality with competitive prices and should design the marketing communication campaigns to promote green products. Rakesh & Nagesh (2014) recommended the recycling of paper, metals, plastics etc in safe and environmentally harmless manner to become more systematized and universal. Commonly used energy efficient lamps and other electrical goods can lead to effective results through green marketing practices. Rambabu Lavuri (2020) revealed consumers yearning towards eco-pleasing with new stocks, which served towards showcasing i.e., sustainable development towards green stock. Ayyappan (2023) recommended businesses showcasing dedication towards sustainability by employing eco-friendly materials, sustainable manufacturing practices and green packaging.
Research Methodology
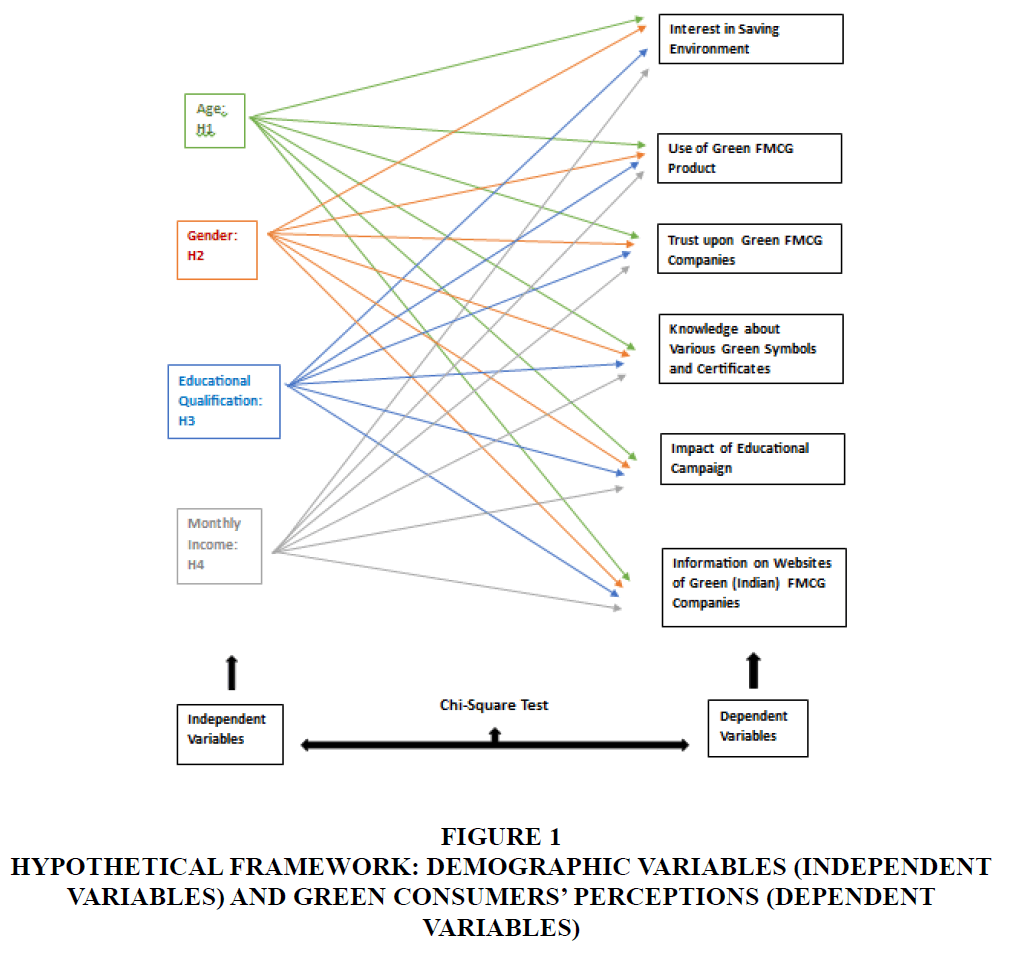
The literature review significantly foregrounded the research gap along with the research problem that was overlooked by previous research studies, i.e., to identify the green consumers’ perception that could influence the decision making of consumers’ for making purchases. Gujarat is the state, well known for its culture and nature loving community, has least studies with regard to the respective research problem. The present study tried to significantly address the gap with research problem. The study tried to fulfil the following research objectives with appropriately designed research methodology Figures 1-4.
Figure 1 Hypothetical Framework: Demographic Variables (Independent Variables) and Green Consumers’ Perceptions (Dependent Variables)
Research Objectives
1. To analyze the association between selected niche demographic variables and green FMCG aware consumers’ perception regarding green marketing practices.
2. To identify the target market i.e., the most influenced group of green FMCG consumers of Gujarat.
3. To establish the conceptual relationship between green FMCG aware consumers’ perception influencing green purchase decision.
The present study adopted a structured questionnaire for collecting data among 368 FMCG consumers of Gujarat who are aware about green marketing practices. The analysis is done with the help of Cross tabulation analysis, Chi-square test and Frequency distribution analysis by adopting convenience sampling technique with descriptive research design. Prior to the final data collection, a pilot testing was conducted among 200 FMCG consumers of Gujarat for comprehensive analysis of identified parameters for consumers’ perception from secondary research.
Analysis and Interpretation
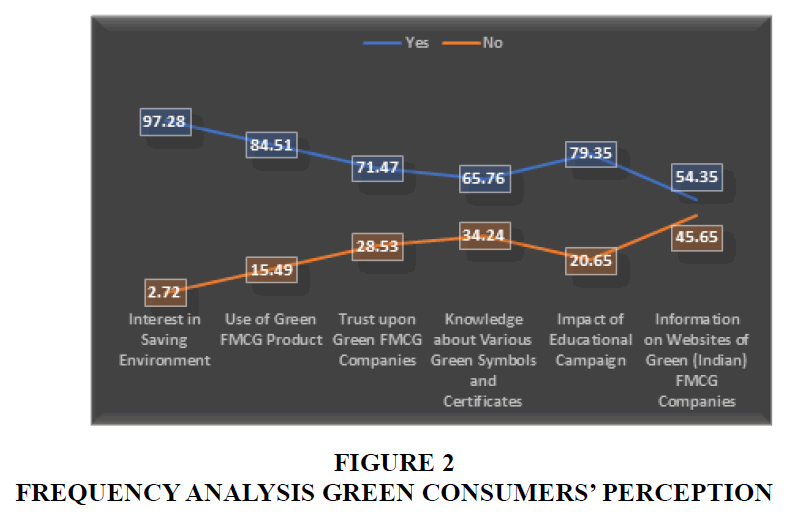
The above framework describes the hypothetical associations between the demographic variables being the independent variables and the selected perceptions being the dependent variables. The study tried analysing these hypothetical associations and identifying the significant associations which can provide a meaningful finding to address the research gap. FMCG consumers are adopting sustainable lifestyles and their consciousness towards environment conservation becomes a significant factor for adopting green products. Consumers frame perspectives by getting influenced from such factors and their perception holds a significant position in their decision making. The present study tried to analyse certain selected green consumers’ perceptions that can ameliorate the green products’ market. Below is the frequency analysis describing the percentage derived upon each selected consumers’ perception towards green FMCG products.
The frequency analysis described the proportion of green FMCG consumers describing their interest in saving environment, their adoption of green FMCG products, their trust upon them along with the impact of educational campaign and company’s website upon their knowledge about various green symbols and certificates. The distribution of responses is positively weighing high for all the perceptions.
Table 1 representing the cross tabulation of niche demographic attributes and dependent variables describing the consumers’ perception. It represents an overview of the green FMCG market of Gujarat.
| Table 1 Cross Tabulation Analysis for Demographic Variables and Green Consumers’ Perception | |||||||||||||
| Demographic Variables | Interest in Saving Environment | Use of Green FMCG Product | Trust upon Green FMCG Companies | Knowledge about Various Green Symbols and Certificates | Impact of Educational Campaign | Information on Websites of Green (Indian) FMCG companies | |||||||
| Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | ||
| Age Group | 15-30 | 174 | 5 | 149 | 30 | 133 | 46 | 118 | 61 | 152 | 27 | 95 | 84 |
| 31-45 | 132 | 5 | 118 | 19 | 92 | 45 | 86 | 51 | 97 | 40 | 71 | 66 | |
| 46-60 | 44 | 0 | 39 | 5 | 33 | 11 | 31 | 13 | 36 | 8 | 29 | 15 | |
| 61 & Above | 8 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| Gender | Male | 201 | 7 | 176 | 32 | 152 | 56 | 146 | 62 | 176 | 32 | 122 | 86 |
| Female | 157 | 3 | 135 | 25 | 111 | 49 | 96 | 64 | 116 | 44 | 78 | 82 | |
| Education Qualification | Less than Graduate | 17 | 1 | 12 | 6 | 13 | 5 | 16 | 2 | 16 | 2 | 11 | 7 |
| Graduate | 131 | 4 | 106 | 29 | 86 | 49 | 73 | 62 | 104 | 31 | 64 | 71 | |
| Post-Graduate | 135 | 4 | 122 | 17 | 108 | 31 | 102 | 37 | 123 | 16 | 85 | 54 | |
| Professional Degree | 75 | 1 | 71 | 5 | 56 | 20 | 51 | 25 | 49 | 27 | 40 | 36 | |
| Monthly Income | 0-25,000 | 134 | 5 | 109 | 30 | 100 | 39 | 84 | 55 | 119 | 20 | 74 | 65 |
| 25,001-50,001 | 87 | 3 | 80 | 10 | 61 | 29 | 62 | 28 | 73 | 17 | 53 | 37 | |
| 50,001-75000 | 51 | 0 | 44 | 7 | 38 | 13 | 33 | 18 | 42 | 9 | 32 | 19 | |
| 75,001-1,00,000 | 33 | 0 | 29 | 4 | 24 | 9 | 20 | 13 | 19 | 14 | 15 | 18 | |
| 1,00,000 & Above | 53 | 2 | 49 | 6 | 40 | 15 | 43 | 12 | 39 | 16 | 26 | 29 | |
The above table 2 describes the chi-square test analysis, mostly applied for categorial data, and analyse the association between variables (Shaun turney, 2022, Chi-Square (Χ²) Tests | Types, Formula & Examples (scribbr.com)). Here, the demographic variables are taken as independent variables and green consumers’ perceptions are taken as dependent variables for analysis. The analysis explained that all the demographic variables are associated significantly with consumers’ perceptions taken for the study. While only gender is found to have no significant association with some perceptions i.e., interest in saving environment, use of green FMCG product and trust upon green FMCG companies. The below table 3 describes the significant associations among demographics and green consumers’ perceptions.
| Table 2 Chi-Square Analysis for Demographics and Green Consumers’ Perception | ||||
| Demographics/Perceptions | Age | Gender | Educational Qualification | Monthly Income |
| Interest in Saving Environment | 0 | 0.109 | 0 | 0 |
| Use of Green FMCG product | 0 | 0.158 | 0 | 0 |
| Trust upon Green FMCG Companies | 0 | 0.117 | 0 | 0 |
| Knowledge about Various Green Symbols and Certificates | 0 | -0.02 | 0 | 0 |
| Impact of Educational Campaign | 0 | -0.003 | 0 | 0 |
| Information on Websites of Green (Indian) FMCG companies | 0 | -0.027 | 0 | 0 |
| Table 3 Significance of Associations between Demographics and Green Consumers’ Perception | ||||
| Demographics/Perceptions | Age | Gender | Educational Qualification | Monthly Income |
| Interest in Saving Environment | Sig. | Not Sig. | Sig. | Sig. |
| Use of Green FMCG product | Sig. | Not Sig. | Sig. | Sig. |
| Trust upon Green FMCG Companies | Sig. | Not Sig. | Sig. | Sig. |
| Knowledge about Various Green Symbols and Certificates | Sig. | Sig. | Sig. | Sig. |
| Impact of Educational Campaign | Sig. | Sig. | Sig. | Sig. |
| Information on Websites of Green (Indian) FMCG companies | Sig. | Sig. | Sig. | Sig. |
The study foregrounded the salient perception that have influenced in purchase decision making with significant groups of consumers. The demographic variables help in identifying the respective group of consumers that are significantly influenced by the perception. The results disclosed all the demographic variables are having significant association with all the perception taken in the study while gender is partially associated with the perception. It has no significant association with ‘Interest in Saving Environment’, ‘Use of Green FMCG Environment’, ‘Trust upon Green FMCG Companies’; while it has significant association with the remaining perception i.e., ‘Knowledge about Various Green Symbols and Certificates’, ‘Impact of Educational Campaign’, ‘Information on Websites of Green (Indian) FMCG companies.’
Discussion & Findings
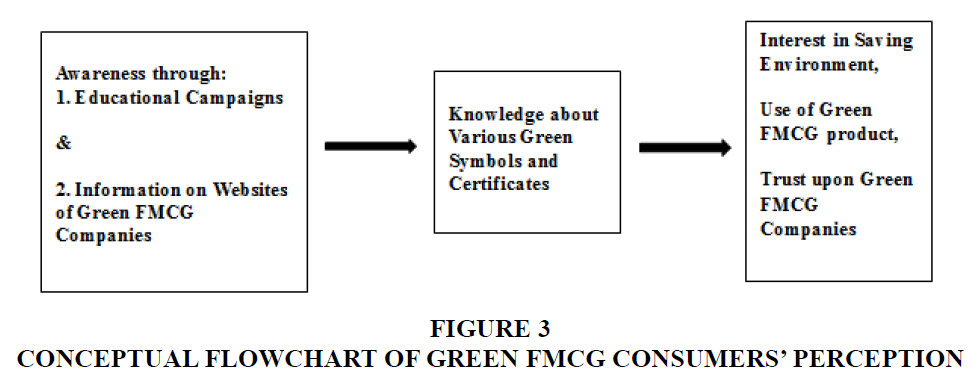
The study highlighted the significant demographic variables with their association on significant perception of FMCG consumers which encourage them to make a purchase decision making. The following flow chart of perception will assist in identifying the impact of one variable (perception) upon another Srinivasan & Lu, (2014).
The above diagram contributes in making a unique linkage between the variables (perceptions) and their dependency upon each other, decodes the direction for marketers to generate marketing strategy dedicated towards green products promotion.
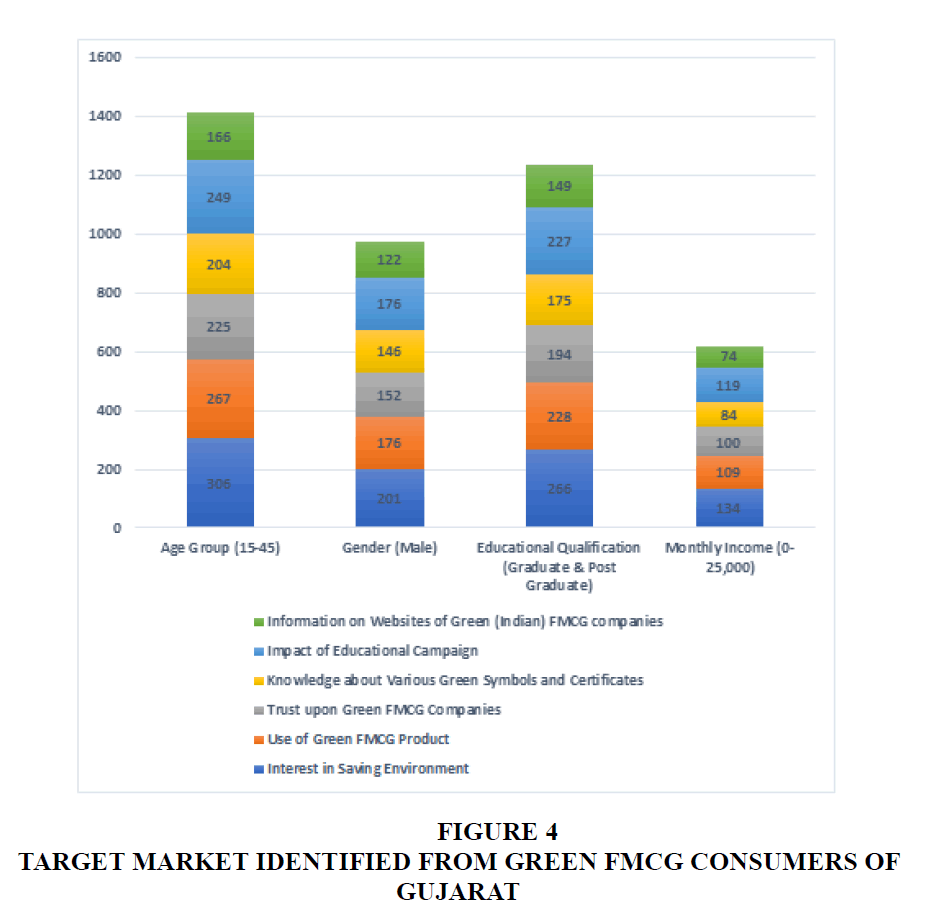
It is important to adopt this variable’s (perception’s) implication by understanding the group of consumers being influenced by them. The following diagram defines the selected target market with their frequency analysis for dependent variable from the results of analysis based on niche demographic attributes and green consumers’ perception. This group of consumers is selected based on their highest frequencies for agreeing positively upon the respective green consumer’s perception. The study has tried to contribute uniquely by describing the group of target audience which marketers can focus upon to expand the reach in market of green FMCG products.
Marketers can also refer to table 1 to identify the gap in adoption of green FMCG products. This will help them in establishing the target where they want to focus for the respective period of time.
Hence, a significant result can be gained by comprehending these perceptions among aware consumers and influencing their purchase decisions. All the demographic variables are found to be significantly associated except gender which is partially associated with the selected consumers’ perception. Therefore, the respective group of consumers can be taken from this process of making their positive perception regarding adoption of green lifestyle and making them adopt a positive purchase decision for green products Sarkar (2021).
This study can contribute by availing marketers the direction for aligning their marketing strategies near these perception and respective target group to make an efficient impact on green FMCG consumers’ purchase decision Wassenhove (2002).
Conclusion
Green marketing is a significant aspect for making successful sustainable development. It is necessary to increase the adaptability of green products by comprehending consumers’ perception which ultimately leads their purchase decision. The study tried to address the direction of consumer’s perception which leads towards adaption of green products. Marketers need to observe consumers’ perception to increase the pace of green marketing practices. For companies to survive in the new era needs focus on green marketing practices as aware consumers are moving and adopting green products only if their needs are addressed appropriately. It is company’s and marketer’s responsibility to position green products as the need of the hour, in order to conserve environment and to make a countable contribution.
References
Ali, A. H., Zalavadia, S., Barakat, M. R., & Eid, A. (2018). The role of sustainability in reverse logistics for returns and recycling. Archives of Business Research, 6(7).
Ayyappan, S., Balaji, S. G., Jayapriya, K., Sawant, P. D., Agarwal, C., & Singh, A. (2023). Awareness Of Green Marketing And Its Influence On Consumer Perception: An Exploratory Study. Resmilitaris, 13(3), 265-276.
Emeritus. (2023). https://emeritus.org/in/learn/sales-and-marketing-green-marketing/
Fouziya, R., & Gracious, J. (2018). Awareness of green marketing and its influence on consumer perception: An exploratory study. Sumedha Journal of Management, 7(2), 62-68.
Hesil Jerda, D.S. (2020). Green Packaging: A Practice of Sustainable Management in consumer perspective. Journal of critical reviews, 2507-2516.
ITC. (2020). ITC. Mumbai: ITC.
ITC. (2021). ITC. https://www.itcportal.com/sustainability/solid-waste-management.aspx
Janda, S., Trocchia, P. J., & Gwinner, K. P. (2002). Consumer perceptions of Internet retail service quality. International journal of service industry management, 13(5), 412-431.
Ker, W., Sen, Y. K., & Rajendran, S. D. (2019). A study on the benefits of eco-friendly packaging on sustainable supply chain management in fast moving consumer goods industry. In E3S Web of Conferences (Vol. 136, p. 04092). EDP Sciences.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Patel, A., Teli, S. N., & Dhumal, Y. (2018). The FMCG Packaging: Moving the Market towards Sustainable Packaging Materials. In Conference: Global Meet on Advances in Design, Materials & Thermal Engineering (pp. 1-6).
Rajamanickam, D. (2022). Customer perception towards green marketing - A study in Namakkal District. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Review, 8(4), 75-81.
Rakesh, H. M., & Nagesh, P. (2014). A study on customer perception of green marketing. International Journal in Management & Social Science, 2(3), 1-13.
Rambabu Lavuri, P. S. (2020). Green Marketing: Factors influence on consumer attitude and perception towards purchasing eco friendly products. American Research Journal of Business and Management, 6(1), 1-11.
Sarkar, J. (2021). Times of India.
Srinivasan, S., & Lu, W. F. (2014). Development of a supporting tool for sustainable fmcg packaging designs. Procedia CIRP, 15, 395-400.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Upgrade. (2023). Retrieved from Upgrade: https://www.upgrad.com/blog/what-is-green-marketing/
Wassenhove, V. D. (2002). The Reverse Supply Chain. Havard Business review, 43. https://hbr.org/2002/02/the-reverse-supply-chain
Received: 28-Sep-2023, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-14047; Editor assigned: 29-Sep-2023, PreQC No. AMSJ-23-14047(PQ); Reviewed: 27-Oct-2023, QC No. AMSJ-23-14047; Revised: 03-Jan-2024, Manuscript No. AMSJ-23-14047(R); Published: 05-Feb-2024