Research Article: 2022 Vol: 14 Issue: 3S
A Conceptual Study on the It Employee's Mental Wellbeing
Thirumal Azagan C, Anna University BIT Campus
Sukesh Kumar S, Anna University BIT Campus
Citation Information: Azagan, C.T., & Kumar, S.S. (2022). A conceptual study on the it employee's mental wellbeing. Business Studies Journal, 14(S3), 1-5.
Abstract
Mental well-being in the IT sector has played a vital part takes place in the performance of an employee. Mental well-being is common in working life which is a struggle to manage for an employee. The main motive of the research study is to investigate the IT employee’s mental well-being in the covid-19 pandemic and that the organizational productivity, performance, and working capability of the individual are influenced by the psychological, physical, and social factors in the personal and workplace environment.
Keywords
COVID-19, IT Employees, Mental Health, Organizational Performance.
Introduction
Mental health wellness includes the employee’s emotional, psychological, and social well-being. Mental wellness or mental well-being affects employees' how they think, feel, and act. It also benefits to employees handle stress, relate to others, and making choices. Mental health is crucial at each stage of employee life, from childhood to adulthood. Throughout life, if employee experiences mental health problems, then the employee’s thinking, mood, and behavior could be affected in the workplace.
Working is good for mental health but the worst organizational culture or working environment can lead to physical and mental health problems. Unemployment is a well-recognized risk factor for mental health problems while returning to, or getting work is protective. (Nataraj, 2019) explains about working environment may lead to physical and mental health problems, harmful use of substances or others, absenteeism, and lost productivity. Workplaces that promote mental health and support people with mental disorders are more likely to reduce absenteeism, increase productivity and benefit from associated economic gains.
In the workplace, there are numerous risk factors for mental health. The majority of risks stem from interactions between the type of work, the organizational and managerial environment, employee skills and competencies, and the support available to help them complete their tasks. For example, an employee may have the skills to complete tasks but lack the resources to do so or unsupportive managerial or organizational practices may exist which affect the mental wellness or well-being of the employee (Giorgi et al., 2020).
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterized by apprehension and symptoms of nervous tension, in which an individual can anticipate impending danger, disaster, or misfortune. The body often moves in response to a perceived threat: tense muscles, rapid breathing, and fast heartbeat. Anxiety can be distinguished from fear both conceptually and physiologically, although the two terms are often used interchangeably for identifiable and specific threats.
Depression
Depression is a negative state which ranges from unhappiness and dissatisfaction to extreme feelings of sadness, pessimism, and disappointment that interfere with daily life. Lack of energy or motivation, difficulty concentrating or making decisions, and withdrawal from social activities. It is the indicator of several mental health disorders (Phadnis et al., 2021).
Stress
Stress is anything that affects the physical and mental state of a normal person. Stress is a reaction to a situation that is not actual. Stress will be more when the demands of the situation are more than the available resources. Psychologists felt that workplace stress to some extent acts as a challenge to the employee when a challenge is met a person feels highly accomplished and satisfied and productivity increases (Prasad et al., 2020). On the other hand, when stress cannot be managed by the employee, productivity decreases, not able to concentrate on the work, and eventually takes the wrong decisions. Hence, stress leads to several issues on mental and physical health.
Burnout
Burnout is a state of physical, emotional, or mental exhaustion accompanied by decreased motivation, decreased performance, and negative attitudes toward self and others. Burnout is most often observed in professionals who work in service-oriented vocations and experience frequent high levels of stress. It can be especially severe in therapists or counselors who work in trauma, who feel overwhelmed by the cumulative secondary trauma of witnessing the effects. Burnout is also experienced by athletes when they are constantly under stress related to performance without adequate reward or without rest. It also over train syndrome and critical exhaustion.
Lay-off
A layoff is an act of the employer to kick off or discharges workers for a temporary or permanent period based on the employee’s actual performance in the organization. A layoff may be a period where the employee can’t take part in other organizational activities without being out fired which may result from worker inefficiency.
Burden
The burden rate has indirect costs associated with employees or payroll costs. The burden caused due to the financial instrument includes payroll taxes, worker’s compensation, paid time off, training, vacation, and sick leave, pension contributions, health insurance, travel expenses, and other benefits. The burden rate shows an original view of total absorbed costs than payroll costs. It doesn’t compare with an individual's or firm's tax burden.
Exhaustion
Exhaustion is a condition in which the employee gets extreme fatigue. Fatigue has been broadly represented as a feeling of tiredness, weariness, or lack of energy. It is commonly corresponding with nonstandard schedules like night shift work and extended work hours that disrupt or shorten sleep.
Sleep Disturbance
Shift work sleep disorder occurs in individuals who work non-traditional hours like split shifts, graveyard shifts, early morning shifts, or rotating shifts. It’s described by a lack of refreshing sleep, excessive sleepiness, and drowsiness. These problems can influence both work and leisure time. The non-traditional work schedule can disturb an employee’s, biological clock or circadian rhythm. The biological clock can have frustrating symptoms when it’s been spontaneous since it affects the employee's sleepiness, body temperature, alertness, hunger, and hormone levels.
Lack of Guidance
Guidance is a direction, advice, and counselling provided in cooperation with the recipient, often using personal data and interviews as important auxiliary tests. Help employees or co-workers to increase their self-awareness about the job role so as to make them more effective as an individual and effective in their job. The guidance provided by the peers helps to improve the skills and knowledge regarding the job. Further, the counselling provided by the peers is an effective and preventive people management strategy for organizations (Shivakumar & Rangaraj, 2020).
Team Pressure
Teamwork in the workplace is a group of individuals or a team works together toward a common goal in an efficient manner. When multiple people work together toward a common goal, your business can flourish but the excessive or stressful demands imagined or real, are made on an individual to think, feel, or act in particular ways. Team pressure at the workplace is inevitable due to the demands of the present-day work environment (Kundi et al., 2020). Team pressure in the organization in which each team has specific time-bounded works to be completed and the inside the team where pressure is created on the individuals to meet the deadline.
Isolation
Isolation is the condition of being separated certain object or place, in our case we consider social isolation. Social isolation is having few people and the lack of social contacts to communicate and spend time with routinely. Some can live alone and don’t feel lonely or socially isolated, and you can feel lonely while being with other people.
Discrimination
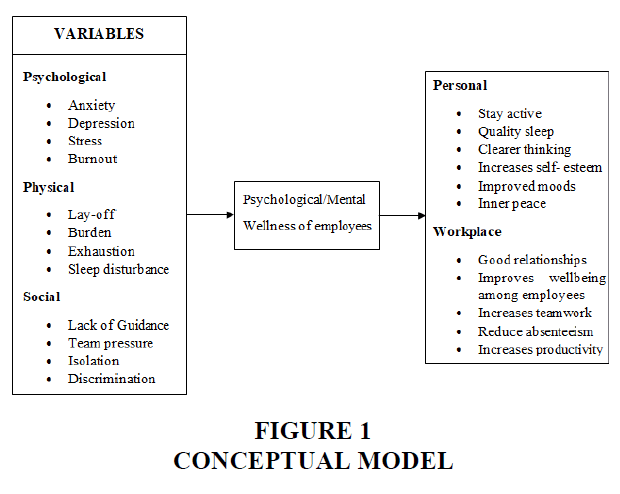
Discrimination is treated unfairly or unequally by different ethnic, religious, national, or other groups (Ranjitha, 2021). Discrimination is usually the behavioral expression of injustice and therefore involves negative, hostile, and injurious treatment of the employees of rejected groups. Discrimination is classified into racial discrimination, sex discrimination, and social discrimination. Discrimination in an organization occurs when a person is treated less favorably compared to others because of a job nature that is not associated with the person’s competencies or the inherent requirements of the job (Figure 1).
Conclusion
To maintain positive mental health wellness employees should get professional help if needed, connect with others, stay positive, get physically active, help others, get enough sleep, and develop skills. Positive mental health wellness confesses employees to realize their full potential, handle stress in the personal and workplace, work productively, and make meaningful contributions to their communities.
References
Giorgi, G., Lecca, L.I., Alessio, F., Finstad, G.L., Bondanini, G., Lulli, L.G., & Mucci, N. (2020). COVID-19-related mental health effects in the workplace: A narrative review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(21), 7857.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Cross Ref
Kundi, Y.M., Aboramadan, M., Elhamalawi, E.M., & Shahid, S. (2020). Employee psychological well-being and job performance: Exploring mediating and moderating mechanisms. International Journal of Organizational Analysis.
Nataraj, I.M. (2019).The Impact of Employee Wellness on Organizational Performance A Study of select IT Organizations.
Phadnis, S., Sengupta, S., & Chakraborty, A. (2021). Work from home, mental health and employee needs: A pilot study in selected information technology organizations in India. Asia Pacific Journal of Health Management, 16(3), 103-110.
Prasad, K.D.V., Vaidya, R.W., & Mangipudi, M.R. (2020). Effect of occupational stress and remote working on psychological well-being of employees: An empirical analysis during covid-19 pandemic concerning information technology industry in hyderabad. Indian Journal of Commerce and Management Studies, 11(2), 1-13.
Ranjitha, R. (2021). Measuring the Mental Wellbeing of E-Workers and Its Impact on E-Work Life Balance during COVID-19 Pandemic. Psychology and Education Journal, 58(4), 718-728.
Shivakumar, B.L., & Rangaraj, T. (2020). Mental wellbeing status of online and work from home women employees with special reference to Coimbatore, Tamilnadu. Public Health, 22, 23rd.
Received: 25-May-2022, Manuscript No. BSJ-22-12075; Editor assigned: 27-May-2022, PreQC No. BSJ-22-12075(PQ); Reviewed: 10-Jun-2022, QC No. BSJ-22-12075; Revised: 13-Jun-2022, Manuscript No. BSJ-22-12075(R); Published: 20-Jun-2022